Transmission Series Part I: Siting Cables in Federal Waters
The following is the first in a two-part series focused on offshore wind energy transmission siting. Part II looks at the design and construction process for a cable connecting to the first two active turbines in federal waters, located off Virginia Beach.
The Biden-Harris Administration has an interagency goal of 30 gigawatts (GW) of deployed offshore wind capacity in the U.S. by 2030, which would unlock a pathway for future deployment of 110 GW by 2050 and beyond. This is complemented with offshore wind energy goals in several Mid-Atlantic states, which are leading the country in building the nation’s renewable energy capacity through offshore wind sources.
Because offshore wind energy is generated over the ocean but consumed on land, efficient transmission of the energy produced offshore to consumers on land will play a critical role in achieving offshore wind deployment goals. Expanding the electric transmission systems and upgrading the onshore grid are necessary components to provide access to offshore wind energy sources in the Mid-Atlantic. The energy generated by offshore wind projects will require underwater transmission cables, called export cables, to traverse through federal and state waters to onshore landing sites, where onshore transmission systems can deliver the power to customers.
Undersea cables are not a new concept - in fact, cables have been installed in the ocean for over 150 years. Cables are typically buried in order to reduce risks to the cables themselves, as well as interactions with ocean users and resources. As previously explored in Ocean Stories, there are telecommunication cables located within U.S. waters throughout the Mid-Atlantic region that are essential for society to function as it does - for example, the trans-Atlantic cables that keep us connected to the internet.
Past experiences with trans-Atlantic cables can be helpful context when conducting offshore wind reviews. However, siting offshore wind transmission cables still requires careful planning, design studies, and cost considerations to minimize environmental impacts and maximize economic value. Each export cable is a custom design for the project, often taking more than a year lead-time to manufacture.
There are generally two technology options considered for export cables: high-voltage alternating current (HVAC) and high-voltage direct current (HVDC). The decision to select HVAC vs. HVDC is highly dependent on a number of factors (e.g., cost, distance, transmission capacity, onshore and offshore space constraints, heat dissipation, electromagnetic fields [EMF]). For example, HVDC cables are able to transmit more energy over greater distances due to reduced electrical losses and higher transfer capability (e.g.,1,200 megawatts [MW] compared to 400 MW per HVAC cable), whereas HVAC cables are usually more economical for offshore wind projects located within 60 nautical miles from shore (as outlined in this New Jersey Board of Public Utilities report). Subsea interconnection cables are also envisioned as a critical component to making our onshore grids more resilient and reliable and delivering renewable energy more efficiently from multiple offshore wind projects to high demand areas.
Basics of Cable Siting
As offshore wind development in the Mid-Atlantic progresses, the need for more cost-effective and efficient transmission options becomes increasingly important. Transmission cable siting is a complex process informed by desktop reviews, routing surveys, and modeling to optimize route options. Often, several cable routing options are identified and then carefully refined through an iterative process to first avoid then minimize risks. Below are a few examples of considerations for siting offshore wind energy transmission cables (“export cables”).
Existing infrastructure. When planning an export cable route, existing infrastructure must be considered. Although an increasing amount of communications are conducted wirelessly, they still rely on a vast network of existing telecommunication cables to transmit large amounts of data rapidly from one point to another. Cables must maintain a certain distance from one another due to heat generated by the power lines and installation safety considerations. Once the cables are operational, these separation distances ensure repairs can be completed without damaging nearby infrastructure. Crossings or overlaps between two cables can be engineered, although this typically requires installing the export cable at a shallower depth to cross over the existing asset and entering into agreements between the asset owners.
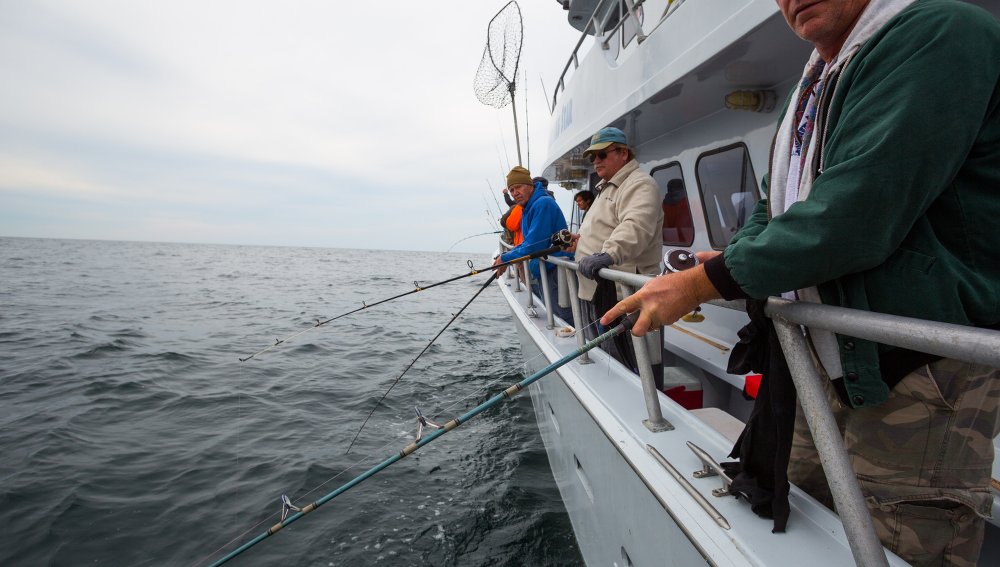

Offshore commercial and recreational fishing. Many wind energy areas (WEAs) and proposed wind projects have some spatial overlap with commercial and/or recreational fishing. This is due in part to the relatively large footprints of both wind development and fishing activities. Many fish populations also are constantly on the move, increasing the possibility of spatial overlap with wind projects. Offshore wind project installation has the potential for resource impacts based on where fish species are located at a given time and could lead to spatial conflicts based on where and when regulated fishing grounds are open for harvest. The type of turbine and proposed layout, prevalent fishing gear types and vessel sizes, and other design, installation, and use considerations are all important factors in identifying preferred project sites and reducing potential conflict. For example, prolonged or widespread seafloor disturbance, electromagnetic fields from cables, and cable scour protection can influence habitat usage by fish and could impact the viability of certain fishing practices.

Wildlife and Habitat. The seafloor has a diversity of geologic features and organisms that are adapted to the unique environment. The sediment of the seafloor can indicate where and which species will thrive in a given area. Shoals, canyons, slopes and artificial reefs provide habitat for marine life of all kinds. There are dozens of deep-sea canyons that cut into the continental slope in the Mid-Atlantic. While some are more well-known, like the Norfolk, Baltimore and Hudson canyons, there are many others that are still relatively unexplored and undocumented. Canyons provide relatively rich biomes comprised of complex benthic habitats and hydrologic conditions, making them suitable locations for cold water corals and sponges to grow and thrive. Larger marine life including large whale species are attracted to the areas’ rich food sources.

Maritime commerce and navigation. The Mid-Atlantic is home to the East Coast’s busiest commercial ports. Accommodating safe access to these ports requires anchorage areas, regularly maintained navigation channels, and aids to navigation which all must be considered in cable route designs.
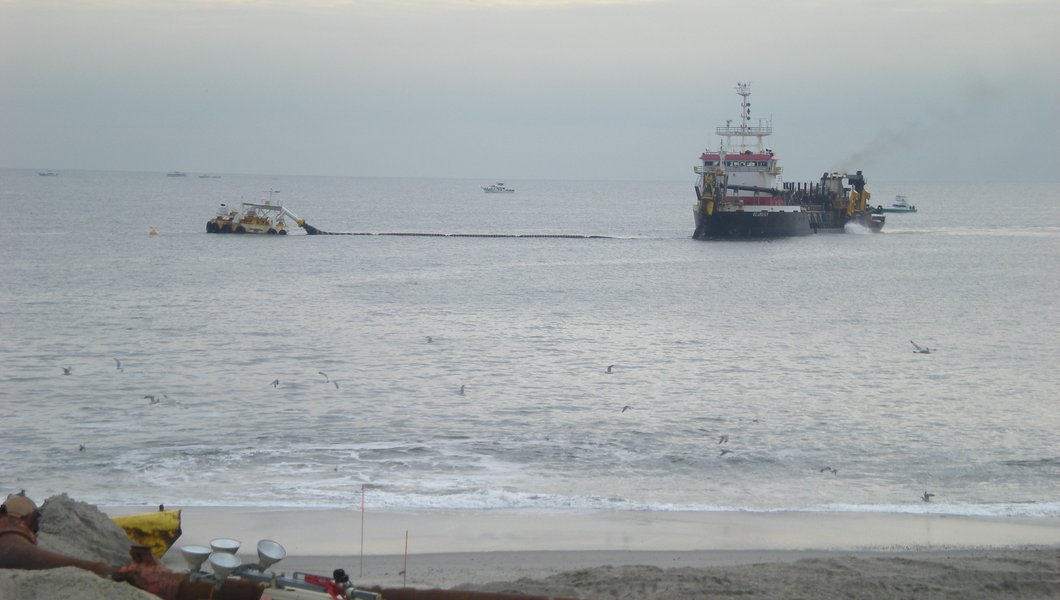

Sand borrow areas. Beach nourishment is the practice of placing sand on the coast to replenish eroded beaches and protect coastal infrastructure from storm damage. Sand for beach nourishment often comes from offshore underwater locations, called “borrow areas.” Cable siting best practices should avoid known borrow areas where possible so that sand harvesting for beach nourishment projects can continue.
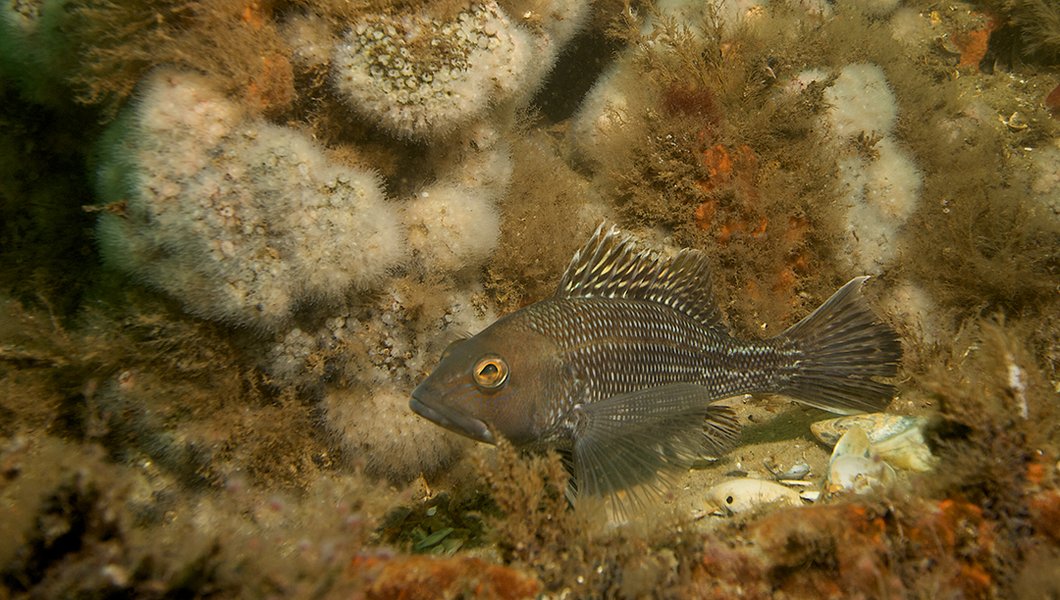

Seafloor composition. The seafloor has diverse sediment types. In some locations, rock outcroppings and large boulders are the dominant geology, while other locations have smaller sediment sizes like gravel, sand, or silt. In many locations, there is a mixture of sediment types. As a general principle, export cables are easier to bury in finer grained sediments than in hard bottom areas. Additionally, hard bottom areas can provide important fish spawning and feeding grounds.
Examples of Ongoing Offshore Wind Transmission Studies that Will Inform Siting
Because of the many uses and resources present in the Mid-Atlantic that are dependent on access to the seafloor, finding a completely “risk-free” cable transmission route is highly unlikely. But careful and coordinated planning can advance offshore wind energy transmission infrastructure in a way that minimizes risk to the environment and existing ocean users. Federal and state agencies have efforts already underway in support of these approaches.
One example is the Atlantic Offshore Wind Transmission Study (AOSWTS), led by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE) Wind Energy Technologies Office (WETO) with analysis conducted by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL). The AOSWTS seeks to evaluate multiple pathways to achieving offshore wind goals through coordinated transmission solutions along the U.S. Atlantic Coast from Maine to South Carolina in the near-term (by 2030) and long-term (by 2050).
This comprehensive transmission analysis will compare the costs and benefits of multiple transmission buildout scenarios (e.g., interstate, inter-regional transmission arrangements, including meshed networks and backbones) under various combinations of electricity supply and demand while considering reliability, resilience, and environmental and siting constraints associated with ocean co-use. The objective of the Study is to elucidate and evaluate multiple pathways for OSW deployment across the Atlantic coast in support of the national goals.
Additional examples of ongoing offshore wind transmission studies:
Spatial Data Product Needs to Help Inform Transmission Siting in Federal Waters
The Mid-Atlantic Regional Council on the Ocean (MARCO) is a partnership that serves as the federally recognized Regional Ocean Partnership for New York, New Jersey, Delaware, Maryland and Virginia. MARCO has an important role in ocean planning and created the Mid-Atlantic Ocean Planning Committee (Mid-A OPC) to coordinate planning activities across federal, state and tribal entities. Recognizing the important role spatial data plays in early planning for offshore wind transmission siting and initial desktop studies, the Mid-A OPC's Offshore Wind Regional Collaborative (OWRC) convened an Offshore Wind Energy Transmission subcommittee that worked to identify the spatial data products and needs that will be most important to transmission siting in federal waters. The subcommittee included representatives from the Department of Energy, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, United States Army Corps of Engineers, New York Department of State, New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection and Delaware Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Control.
The OWRC subcommittee identified the spatial datasets most important to transmission siting in federal waters. The subcommittee then prioritized data products to be considered by the MARCO Board to add to the Mid-Atlantic Ocean Data Portal. By highlighting these opportunities to update or enhance data products, OWRC members and other partners are working to ensure that offshore wind transmission siting continues to be informed by the best available and most useful science and data.
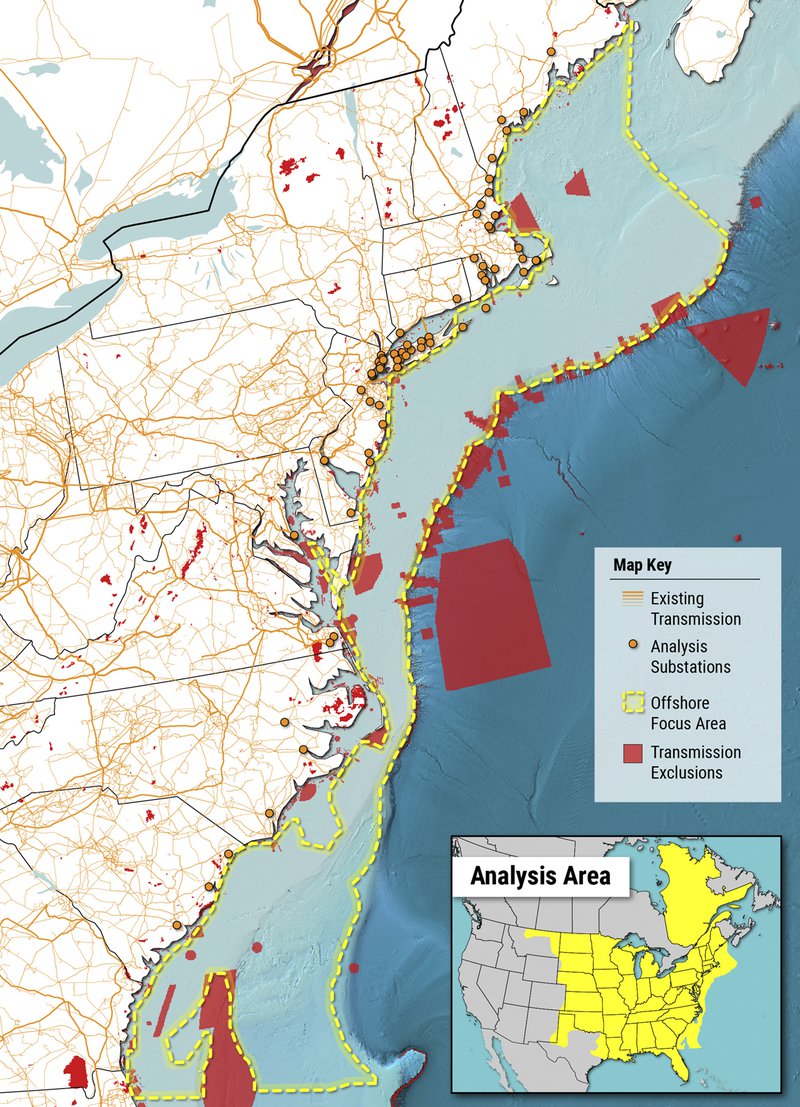
To guide its discussions, the OWRC identified a study area based on where transmission cables in federal waters are anticipated to be sited over the next 5-10 years. The study area boundaries followed the 3-nautical-mile state/federal waters boundary on the landward side, the 2,600-meter bathymetry contour on the seaward side, and the federal Outer Continental Shelf (OCS) administrative boundary between New York and Rhode Island to the north, and between Virginia and North Carolina to the south. This area included active offshore wind projects; however, the subcommittee's assessment is meant to be applied to future lease or call areas, not current proposals.
The subcommittee identified and prioritized 33 transmission siting challenges within those boundaries. Each challenge was ranked by subcommittee members as “high, medium, or low,” based on how important or significant the challenge is anticipated to be in the process of siting transmission cables for offshore wind energy. Then, a desktop review of the Portal was conducted to evaluate the availability of information related to each challenge. Challenges that were assigned high importance by subcommittee members and low data availability on the Portal will lead to recommended data products for the Portal.
Conclusion
The subcommittee’s analysis showed the Portal already contains a significant amount of high-quality spatial data needed to avoid or minimize transmission siting challenges in federal waters. Out of the few challenges that ranked high importance with medium or low data availability, most can be easily addressed. For example, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Placement Areas layer shown above was added to the Portal to display sites at sea and along the coast that the agency relies on to deposit materials from channel dredging and other important public works projects. These results will inform the OWRC and Portal work plans, including future outreach and coordination efforts as well as data product development.
You can learn more about MACO’s OWRC work group initiatives and MARCO’s State initiatives on our website. The Portal contains thousands of map layers and additional informational materials to explore, including a Current Agency Actions and Public Comment Opportunities page that tracks offshore wind activities in the region.
To stay up to date on events and notifications you can sign up for MARCO’s quarterly newsletter and view our events calendar. You can also click here to sign up for updates on the latest Portal data additions and tool enhancements.
This story was produced by the Mid-Atlantic Regional Council on the Ocean, Delaware Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Control, Monmouth University Urban Coast Institute, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection, New York State Department of State, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, and U.S. Department of Energy.


